Department for Education (DfE) Reproducible Analytical Pipeline (RAP) Strategy Implementation Plan 2023
The Analysis Function Reproducible Analytical Pipelines (RAP) Strategy was published in 2022. The strategy sets clear aims and actions for analysts and analyst leaders in government to implement RAP into their default ways of working. Reproducible Analytical Pipelines are automated, analytical processes that incorporate elements of software engineering best practice to ensure that pipelines are:
- reproducible
- auditable
- efficient
- high quality
RAP improves the value, efficiency and quality of outputs when it is used appropriately within statistical and analytical processes.
The DfE has been encouraging and supporting the use of RAP for statistics production since roughly 2015. We made the transition to start publishing statistical releases through “Explore Education Statistics” in 2020. This provided a model to further facilitate and take benefits from implementing RAP at scale. In that time, extensive guidance for all analysts working on statistics production and publication has been developed and we have seen huge progress in RAP uptake and culture.
There is currently a clear expectation at DfE that any analyst working in statistics production should know RAP principles and be able to implement them using the recommended tools to meet at least the department’s definitions of “good” and “great” practice. Teams who do not currently meet this baseline are receiving the necessary support to do so.
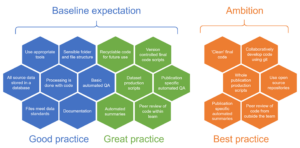
The diagram shows the baseline expectation of analysts at DfE. It gives examples of “good practice”, such as:
- using appropriate tools
- using sensible folder and file structure
- ensuring all source data is stored in a database
- ensuring all processing is done with code
- ensuring files meet data standards
- ensuring work is fully documented
It gives examples of “great practice”, such as:
- creating recyclable code for future use
- producing version controlled final code scripts
- producing dataset production scripts
- producing publication specific automated quality assurance (QA)
- creating automated summaries
- ensuring code produced by members of the team is peer reviewed by others in the team
The diagram also show DfE’s ambition for the future and gives examples of “best practice”, such as:
- creating “clean” final code
- working with colleagues to develop code using Git
- creating whole publication production scripts
- using open source repositories
- creating publication specific automated summaries
- ensuring code produced by members of the team is peer reviewed by colleagues outside of the team
Our goals
In 2023 and beyond, our goals are to:
- expand the breadth of our RAP expectations, guidance and support to include wider analytical roles and purposes
- continue to monitor and improve RAP progress in statistics production and publication
This implementation plan will outline what actions we plan to undertake starting in 2023 to meet all elements of the RAP strategy that are applicable to us. At a high level these are to:
- introduce RAP development plans for all statistics production and publication pipelines that outline how the current processes compare to the baseline RAP expectation
- develop and expand our existing guidance to cover all analysis, including that of wider analytical roles and professions
- continue to provide in-person workshops to improve capability in the department
- continue the RAP knowledge-share series — this enables analysts to share their RAP successes and benefits with colleagues, as well as building awareness and growing RAP culture
- expand existing manager and leader specific guidance and training to set clear expectations — this will empower managers and leaders to build RAP into their team’s projects and promote a RAP by default approach in their areas
- expand the RAP champion network within DfE to cover all areas of analysis — this will mean that analysts, analyst managers and analyst leaders in all areas will have a clear and visible representative for RAP
Current state: summary at the end of 2022
Tools
The DfE software centre provides multiple options for the recommended tools to develop RAPs. Our guidance is that SQL, R and Git are the recommended tools for RAPs in statistics production and publication. This is because they are widely used in the workforce and there is extensive existing guidance for these tools. However, Python is also available. We provide Azure DevOps project areas for internal or sensitive RAP development repositories, and the dfe-analytical-services GitHub area hosts all public code.
In 2020 the Department launched Explore Education Statistics (EES). This is our own statistics publication platform that requires common open data standards for all published data and statistics. Since transitioning to EES, we have seen a significant improvement in RAP uptake and capability. This is because EES concentrates on open data standards, whilst also stripping out a large proportion of the typical statistics production process. This includes, for example, formatted Excel tables. The open data is also easily reusable for other services or dashboards.
Capability
DfE has well-established and extensive guidance for RAP, which concentrates mainly on statistics production and publication. There is also an internal RAP self-assessment tool for statistics production. Each team responsible for accredited official statistics and official statistics publications uses the self-assessment tool to record their progress regularly.
The central Statistics Services Unit also function as a dedicated resource to support and facilitate RAP development. For example, in 2022 the Statistics Services Unit started running in-person technical skills workshops for colleagues. The first workshop topic was about using Git with GitHub and Azure DevOps. The Statistics Services Unit also run a knowledge-share series which covers a different RAP topic each month. The chosen topic relates to areas we feel need development based on our internal RAP self-assessment tool. Volunteers present their own RAP successes at the knowledge-share sessions, which have been well attended by analysts in a variety of areas and roles. We have also received positive feedback about these sessions.
The central support unit have offered a “partnership programme” since late 2020. The partnership programme offers teams the opportunity to ask for support from the Statistics Development Team (SDT) to help them improve their statistical processes. The SDT will provide additional resource and expert support to help them improve their capability. The type of support will depend on the needs of each team, but can include things like:
- bespoke upskilling
- training on writing tailored example code
- regular check-ins
There will be a scoping exercise at the beginning of a partnership to define:
- the resource needed from both SDT and the partnering team
- milestones
- success criteria
These metrics and criteria will be reviewed throughout the partnership. Partnership programmes are run on request and based on capacity.
Culture
The DfE’s chief analyst is the department’s Senior Civil Service (SCS) lead for RAP. The Statistics Development Team have also been championing RAP in the department for a long time. This means that the official statistics production and publication area has achieved a lot including:
- defining an established baseline expectation
- making lots of support and learning resources available to colleagues
- building a positive RAP culture
However, we are aware that RAP is not as widely encouraged in other areas of analysis. To address this, we are now planning to build on the achievements seen in statistics production and publication to expand to all analysis. In 2023 we are aiming to recruit RAP champions across all areas of analysis and form an active network that has a wide reach across the analytical professions.
Implementation Plan
Objective: Provide guidance for tools
Analyst leaders will work with security and IT teams to give analysts access to the right tools.
Supporting activity 1
Develop and share online guidance which defines:
- what tools are accessible
- what each tool is for
- when it is appropriate to use each tool
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when:
- analysts know which are the right tools to use for a project
- tools and guidance about the tools are easily available to analysts
Supporting activity 2
Make tool guidance a standard part of analytical introductions.
Timeframe for completion
This work is part of a long-term project.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when:
- managers and leaders are aware of what tools new starters will need and can give support to access them
- the right information is available in analytical induction packs
Objective: Develop IT platforms
Analyst leaders will work with security and IT teams to develop platforms that are easy for analysts to access, and flexible and responsive to the needs of analysts.
Supporting activity
Work with the Data Directorate and IT to ensure that analytical needs are considered in the department’s future data and IT strategies. This especially relates to analytical needs around creating and maintaining RAPs.
Timeframe for completion
This work is part of a long-term project.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when:
- analytical needs are understood, where needed
- future data and IT strategies take RAPs into account
Objective: Ensure access to the right tools
Analyst leaders will work with security, IT, and data teams to make sure that the tools data analysts need are available in the right place and are easy to access.
Supporting activity
Ensure all necessary tools are available in the software centre.
Timeframe for completion
This work has been completed.
Success criteria
Analysts can now independently download all necessary software from the software centre as needed without needing support from IT.
Objective: Use open-source tools
Analysts will use open-source tools when appropriate.
Supporting activity 1
Give a knowledge-share session on what open-source tools are appropriate for which tasks.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the short-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when over 70% of analysts can use open-source tools for their analysis. This can be measured using:
- available repositories
- self-assessment tools and surveys
- RAP logs
- workday skills capture
Supporting activity 2
Develop and publicise existing written guidance to ensure there is clarity on the most appropriate open-source tools and give information about best practice for how to use them.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when over 70% of analysts can use open-source tools for their analysis. This can be measured using:
- available repositories
- self-assessment tools and surveys
- RAP logs
- workday skills capture
Objective: Open source code
Analysts will open source their code.
Supporting activity 1
Develop existing guidance on open-source repositories to ensure clarity on when, how, and why it is appropriate to open-source code safely. For example, this includes explaining why public dashboards code is being hosted on GitHub.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when analysts know when it is appropriate or expected that they:
- open-source their code on GitHub
- use Azure DevOps to share internally when it is not possible to open-source publicly
Supporting activity 2
Include code which is being open-sourced as a part of the standard sign-off process. Provide guidance to support the leadership team to know how to make code open safely.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when code sign-off is a part of standard sign-off processes for publication.
Supporting activity 3
Continue to provide in-person workshops on using Git, GitHub, and Azure DevOps.
Timeframe for completion
This work is ongoing.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when analysts know how to open-source code using best practices, and when it is appropriate to do so.
Objective: Version and store source data
Analysts will work with data engineers and architects to make sure that source data are versioned and stored so that analysis can be reproduced.
Supporting activity 1
Facilitate a knowledge-share session with data engineering colleagues to improve shared knowledge and relationships.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the short-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when analysts and data engineers have an improved understanding of each other’s roles and needs.
Supporting activity 2
Analysts engage in IT and data strategy and planning to ensure future projects meet analytical needs.
Timeframe for completion
This work is part of a long-term project.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when future IT and data strategies are developed to meet analysts needs and when these strategies improve current processes.
Objective: Plan RAP learning and development time
Analyst leaders will ensure their analysts build RAP learning and development time into work plans.
Supporting activity 1
Leaders will engage with leadership-specific RAP training, which will be launched in late 2023.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the short-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when leaders:
- actively promote RAP learning and development (L&D) opportunities and resources
- set clear expectations that all analysts should be dedicating time to upskilling and improving projects
Supporting activity 2
Leaders will make L&D budgets available where more niche opportunities for development arise which would complement existing RAP support.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the short-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when analyst leaders are prioritising RAP skills and approving requests to the L&D budget for RAP related skills development.
Objective: Share knowledge
Analyst leaders will help their teams to work with Digital Data and Technology (DDaT) professionals to share knowledge.
Supporting activity 1
Hold joint a knowledge-share session for members of DDaT and analysts.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the short-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when we have held a joint knowledge-share session with participants from both analysis and DDaT.
Supporting activity 2
Extend all invitations to RAP sessions and L&D opportunities to DDaT colleagues as well as analysts.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the short-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when colleagues from DDaT are included in all RAP L&D opportunities.
Objective: Create time to use new skills
Analyst managers will build extra time into projects to adopt new skills and practices where appropriate.
Supporting activity 1
Ensure the Statistics Development Team engage with analyst managers for “RAP development plans” which clearly outline timelines and expectations for RAP projects.
Timeframe for completion
This work is ongoing.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when:
- teams can provide documented RAP development plans when asked
- managers and leaders check RAP development plans at the sign-off stage
Supporting activity 2
Ensure teams:
- hold a RAP planning session at the start of any new projects
- include RAP reviews in wash-up sessions using the RAP section of the quality assurance (QA) tool
Timeframe for completion
This work is part of a long-term project.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when:
- teams can provide documented RAP development plans when asked
- managers and leaders check RAP development plans at the sign-off stage
Objective: Learn how to manage RAP projects
Analyst managers will learn the skills they need to manage RAP projects.
Supporting activity
Ensure the Statistics Development Team facilitate manager-targeted workshops for relevant skills, such as Git and version control, and R.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when we have given manager-specific workshops in all DfE locations on:
- Git and version control
- using R for RAP
Objective: Learn skills to use RAP principles
Analysts will learn the skills they need to implement RAP principles.
Supporting activity 1
Continue the RAP knowledge-share series to cover all skills needed to implement RAP. The topics will be prioritised by demand.
Timeframe for completion
This work is ongoing.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when:
- knowledge-share sessions are well attended
- slides and recordings from knowledge-share sessions are saved resources that are available to all analysts
Supporting activity 2
Develop online guidance pages to include :
- information about which skills are relevant for each RAP principle
- links to relevant training or L&D resources for each RAP principle
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when we see improvements in the skills needed for RAP through RAP surveys and the HR skills capture.
Supporting activity 3
Analysts will use professional L&D budget for requests for any niche development opportunities that may complement existing RAP support.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when analysts request L&D opportunities related to RAP skills using the analytical professional L&D budgets.
Objective: Choose leaders to promote RAP
DfE will choose leaders responsible for promoting RAP and monitoring progress towards this strategy within organisations.
Supporting activity 1
Assign a Senior Civil Service (SCS) lead for RAP.
Timeframe for completion
This work has been completed.
Success criteria
The department now has a visible SCS lead who promotes RAP and reviews regular updates on the progress of the department.
Supporting activity 2
Nominate RAP champions in all areas of analysis.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the short-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when RAP is represented and championed in all areas of analysis.
Objective: Create multidisciplinary teams
DfE will form multidisciplinary teams that have the skills to make great analytical products, with some members specialising in developing analysis as software.
Supporting activity
Improve relationships between data engineers, DDaT professionals and analysts through knowledge-sharing and working together on IT and data strategies.
Timeframe for completion
This work is ongoing.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when teams of different professions are more connected and have improved relationships.
Objective: Promote “RAP by default” approach
Analyst leaders will promote a “RAP by default” approach for all appropriate analysis.
Supporting activity 1
Encourage the use of RAP elements in Quality Assurance (QA) logs and set clear expectations for RAP progress.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when analyst leaders are asking to see RAP logs alongside QA logs in sign-off processes.
Supporting activity 2
Engage with RAP champions and promote a “RAP by default” approach.
Timeframe for completion
This work is part of a long-term project.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when leaders build awareness of RAP, set expectations and promote knowledge-sharing within their areas.
Objective: Create strategic plans
Analyst leaders will write and implement strategic plans to:
- develop new analyses with RAP principles
- redevelop existing products with RAP principles
Supporting activity 1
Incorporate RAP into wider strategic planning and prioritise it.
Timeframe for completion
This work is part of a long-term project.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when RAP is considered in wider strategic planning and incorporated into this planning.
Supporting activity 2
SDT add RAP principles into existing department analytical QA logs.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when leaders and teams in all areas make use of RAP elements in the QA log to:
- review existing pipelines
- identify opportunities to benefit from RAP
Supporting activity 3
Leaders set the expectation that teams should:
- evaluate existing processes
- create RAP development plans
- record and report progress for leaders in the new tool
Timeframe for completion
This work is ongoing.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when leaders and teams in all areas make use of RAP elements in the QA log to:
- review existing pipelines
- identify opportunities to benefit from RAP
Objective: Advise analysis teams how to use RAP
Analyst leaders will lead their RAP champions to advise analysis teams on how to implement RAP.
Supporting activity
Engage with RAP champions and promote RAP guidance and resources.
Timeframe for completion
This work is part of a long-term project.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when leaders in all areas:
- are aware of their RAP champions
- engaged with their RAP champions
- can refer their analysts to a RAP champion
Objective: Incorporate RAP development into workplans
Analyst leaders will help teams to incorporate RAP development into workplans.
Supporting activity 1
SDT work with RAP champions to develop RAP development plan template and guidance for all analytical areas.
Timeframe for completion
This work is part of a long-term project.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when teams use RAP development plans and share successes and case studies in knowledge shares or blog posts.
Supporting activity 2
Leaders work with RAP champions to promote and support RAP development plans.
Timeframe for completion
This work is part of a long-term project.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when teams use RAP development plans and share successes and case studies in knowledge shares or blog posts.
Objective: Identify most valuable projects for RAP
Analyst leaders will identify the most valuable projects by looking at how much capability the team already has and how risky and time-consuming the existing process is.
Supporting activity 1
SDT and RAP champions share a form throughout the department with statements about RAP processes to gain understanding of most valuable projects across all areas.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the short-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when leaders and RAP champions approach teams with most valuable projects to begin RAP development plans.
Supporting activity 2
Leaders use a variety of methods and resources to identify projects in their areas that would benefit the most from RAP. These methods and resources include:
- guidance
- self-assessment tools
- RAP logs
- form responses
- knowledge from RAP champions
Timeframe for completion
This work is ongoing.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when leaders and RAP champions approach teams with most valuable projects to begin RAP development plans.
Objective: Evaluate RAP projects
Analyst managers will evaluate RAP projects within organisations to understand and demonstrate the benefits of RAP.
Supporting activity 1
SDT develop guidance for managers on RAP expectations and benefits.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when we have developed and shared guidance specifically targeted at analytical managers and leaders, which explains RAP expectations and benefits.
Supporting activity 2
Organise a knowledge-share series that concentrates on demonstrating the benefits of RAP.
Timeframe for completion
This work is ongoing.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when we have developed a culture of sharing information between teams about the improvements and benefits brought about RAP.
Objective: Use RAP principles wherever possible
Analyst managers will mandate that their teams use RAP principles whenever possible.
Supporting activity
SDT run manager specific workshops to help understanding of manager-level expectations and skills.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when managers have the knowledge and skills necessary to support their team in implementing RAP.
Objective: Demonstrate value of RAP principles
Analysts will engage with users of their analysis to demonstrate the value of RAP principles and build motivation for development.
Supporting activity
We will outline these activities in a separate user engagement strategy.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Objective: Produce analysis using RAP
Analysts will produce their analysis using RAP.
Supporting activity 1
SDT develop guidance outlining expectations for implementing RAP within each analytical role.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when analysts know how RAP principles can and should be applied to their work in all types of analytical roles.
Supporting activity 2
Continue running knowledge shares and in-person workshops to facilitate L&D for RAP skills.
Timeframe for completion
This work is ongoing.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when analysts feel supported in developing the skills needed to implement RAP.
Objective: Support leaders to champion RAP
RAP champions will support leaders in their organisation in achieving this strategy by acting as mentors, advocates, and reviewers.
Supporting activity 1
Recruit RAP champions representative of all areas of analysis.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the short-term. We will then continue to recruit RAP champions on an ongoing basis.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when we have formed a RAP champions group of analysts from all areas of analysis.
Supporting activity 2
Make RAP champions visible. Include the “RAP champion” title included in delve profiles and make a list of champions easily available in appropriate places, such as the analytical Microsoft Teams channels and the DfE intranet.
Timeframe for completion
This work will be completed in the medium-term.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when analysts know:
- who their RAP champions are
- that RAP champions are mentors, advocates, and reviewers
Supporting activity 3
RAP champions encourage progress in their area by:
- sharing knowledge and guidance
- tracking progress
- encouraging and supporting RAP implementation
Timeframe for completion
This work is ongoing.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when all areas have a RAP champion who actively encourages RAP implementation and progress.
Objective: Create peer review schemes
RAP champions will manage peer review schemes in their organisation to facilitate mutual learning and quality assurance.
Supporting activity
RAP champions develop and roll out a peer review scheme.
Timeframe for completion
This work is part of a long-term project.
Success criteria
We will have achieved success when a formal peer review scheme is:
- rolled out
- used by analysts on demand
