Role profile: mathematical modeller
Mathematical modellers support teams and programmes of work by using their technical understanding of modelling, simulation and statistics. They work in dedicated teams or in multidisciplinary analytical teams.
Mathematical modellers usually have experience of working in a numerate role, or a qualification in a numerate subject. They will have an awareness of mathematical modelling tools and programmes.
Typical role responsibilities
Mathematical modellers:
- develop and use analytical models and techniques – they often use spreadsheets, databases, and other pragmatic approaches to solve problems numerically
- identify, use and analyse complex data-sets – this includes synthesising multiple evidence sources and using a range of software, including data-base and statistical packages
- develop and follow protocols for managing the development of models
- produce and communicate analysis
Skills
There are several important skills that mathematical modellers need to be successful in their role.
Find out more about skill level definitions.
You must have a strong understanding of mathematical and statistical modelling approaches.
You will be expected to demonstrate these skills at different levels depending on the seniority of your role.
Mathematical modeller
As a mathematical modeller, you must have a ‘practitioner’ skill level.
Senior mathematical modeller
As a senior mathematical modeller, you must have an ‘expert’ skill level.
Head of mathematical modelling
As a head of mathematical modelling, you must have a ‘working’ skill level.
You must have excellent communication and interpersonal skills. You must be able to clearly and confidently communicate complex analysis to specialists and non-specialists both verbally and by using visualisation techniques.
You will be expected to demonstrate these skills at different levels depending on the seniority of your role.
Mathematical modeller
As a mathematical modeller, you must have a ‘practitioner’ skill level.
Senior mathematical modeller
As a senior mathematical modeller, you must have an ‘expert’ skill level.
Head of mathematical modelling
As a head of mathematical modelling, you must have a ‘working’ skill level.
You must be able to run models in software packages.
You will be expected to demonstrate these skills at different levels depending on the seniority of your role.
Mathematical modeller
As a mathematical modeller, you must have a ‘practitioner’ skill level.
Senior mathematical modeller
As a senior mathematical modeller, you must have an ‘expert’ skill level.
Head of mathematical modelling
As a head of mathematical modelling, you must have a ‘working’ skill level.
You must be able to use analytical skills and analytical software to present well-founded results and recommendations to support decision making.
You will be expected to demonstrate these skills at different levels depending on the seniority of your role.
Mathematical modeller
As a mathematical modeller, you must have a ‘practitioner’ skill level.
Senior mathematical modeller
As a senior mathematical modeller, you must have an ‘expert’ skill level.
Head of mathematical modelling
As a head of mathematical modelling, you must have a ‘working’ skill level.
Sample career path
The mathematical modeller career path shows some of the common entry and exit points for the role. It also shows the typical skill levels needed.
You can enter a mathematical modeller role from another analytical profession, or from other professions. You can also exit the role to join another profession.
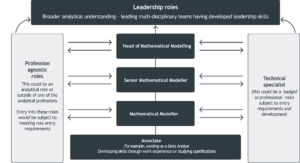
The diagram shows a potential career path. It shows that you can enter or leave a role from a wide range of backgrounds and experience levels. For example, you could become a mathematical modeller by developing your skills in an associate role. You could continue to move up the levels in the career path by taking on more senior mathematical modeller roles. Or you could develop your skills by working in a technical specialist role in an analytical or digital profession. You could also develop the necessary skills by working in a profession agnostic role outside of these professions.
A role that could be done by any person with the relevant skills or experience from any profession.
This could be a ‘badged’ or professional role that is subject to entry requirements and development.
Beyond the head of mathematical modelling role, you could go into more senior leadership roles. These roles require broader analytical understanding, and the ability to lead multi-disciplinary teams.
